PURPOSE OF ROTATIONAL CAPACITY TESTING: THEN AND NOW
Rotational Capacity test, or ROCAP, was originally developed to ensure the presence of lubrication on Hot dip galvanized coated fasteners for structural products.

HDG (zinc) on steel fasteners is a sticky coating leading to very high friction being developed during installation. The use of lubricated nuts reduces friction and avoids galling during assembly.
The lubricant has a color tracer included to readily identify that the nut has been lubricated. The color of the lubricant is not specified in the spec, so we can find several colors on the market, depending on the supplier. You can recognize an Infasco lubricated nut by its pinkish red color.
ASTM A325 specification did not require a specific friction requirement or range, it simply requires the presence of the lubricant. Due to the limitations of this specification, it was revised and replaced by ASTM F3125 in 2015.
To have a better understanding of ROCAP testing procedure, we will start at the beginning. Let’s take a closer look to the steps as per the now retired ASTM A325-14 standard.
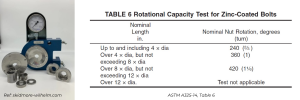
As per the now retired ASTM A325-14 standard, here are the ROCAP Testing Procedure steps:
1. Install bolt in Skidmore with 3-5 threads in the grip.
2. Tighten to 10% of proof load.
3. Rotate nut until specified degrees of rotation are achieved per the specification. Eg. ½-13x 2 ½ equals 5 diameters requiring 360 degrees rotation.
It’s quite simple; the fastener assembly failed the test if:
- Bolt breaks before full rotation.
- Inability to remove nut after rotation.
- Shear failure of threads occur.
Rotational capacity is a very severe test. The nut is rotated beyond the yield point of the bolt. Plastic deformation of the bolt is normal, expected and is acceptable.
But the Rocap Test as per A325-14 had some limitations as:
- Test for proper lubrification only.
- In Canada, construction projects tend to use torque tightening.
-
- Exception: BRIDGE construction sites use turn of nut method.
- Torque tightening can lead to wide scatter in the bolted joints’ final tension.
- ROCAP per A325, as well as A490, test for frictional rotation in a load sensing device and yet do not have any pass/fail criteria for tension.
Therefore, the ASTM F3125 specification was created, which combines all structural bolts under a single spec; A325, A490 A325M, A490M, F1852, and F2280 (twist off bolts). The spec also expanded and clarified what coatings could be applied and also defined nut over tap limits.
With this new specification the ROCAP test became much tougher as well more meaningful. It not only sets friction parameters but also has a minimum tension requirement. We will cover the ASTM F3125-19 Rotational Capacity Testing in depth in our next article.
Don’t miss it! Subscribe to our newsletter to receive first, our next article on ASTM F3125-19 Rotational Capacity Testing: A to Z.
